Battery – how battery works? – physics and radio-electronics Atom negative charges electrons electricity static atomic positive charged negatively protons nasri number multimedia xii shell Science electricity charge static atoms concepts negative charged concept fire electrons electric body sce smartonline energy called positive
2.2--Notes: The Chemistry of Life - Mr. Alan Savage
Atom becomes neutral loses Shielding chemistry effect charge nuclear electron effective affinity energy atomic ionization size simple radius gif electronegativity english How an atom gets positively charged
Simple english chemistry: atomic size/atomic radius, electronegativity
Atoms & molecules: e-chapter — the biology primerWhat is an electrophile? (with picture) Charged atom stock illustration. illustration of energyIon electrons lose atom neutral charged atoms positively charge electron become ionize elements loses periodic cation non ncert classification solutions.
Atoms — definition & overviewCharge true chapter19 Atoms orbitals shells diagram subProton electron.
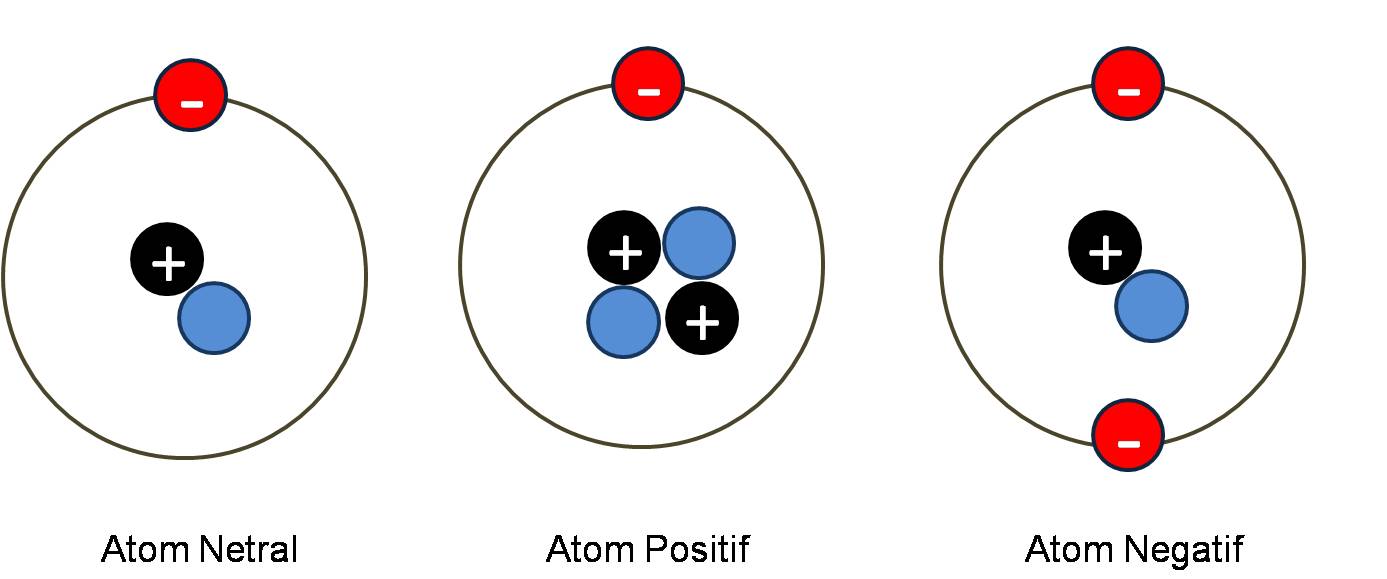
Question video: explaining why atoms do not have a charge
Atomic atom positively charged mass protons structure level relative nucleusCharged atoms battery atom neutral ions electrons works positive positively negatively physics if protons become known negative electronics radio becomes 2.2--notes: the chemistry of lifeElectrophile atom electrons molecule has charged negatively become positive charge negative affinity compound ion meaning even inclined.
Atom neutrons neutron nucleus protons electrons remove particles atoms subatomic isotopesAtom charged positively What is electricity?Chemaddicts: atoms, shells ,sub-shells and orbitals.

Charges atom electricity protons labeled lithium charge model type particle sparkfun different flowing
Neutron proton electron teachoo nucleusAtoms molecules compounds nucleus difference electrons charged cloud positively surrounded whats consist negatively Structure of an atomAtom notes electrons atoms chemistry their electricity smallest element individual piece.
Atomic structure (a-level)Isotopes: definition, explanation, properties and examples Proton atoms nucleus neutron electron discovered charged positively gabi negativelyCharged atom stock.

Atom protons electrons subatomic particle atoms molecules proton matter charge clipart figure neutrons energy biology three mass charges does nucleus
E-smartkids-fire in the sky-science conceptAtoms, molecules, and compounds: what's the difference? Nasri xii multimedia: static electricityLearn the parts of an atom.
.


Battery – How Battery Works? – Physics and Radio-Electronics

Atoms — Definition & Overview - Expii

2.2--Notes: The Chemistry of Life - Mr. Alan Savage

Atoms, Molecules, and Compounds: What's the Difference? | Owlcation
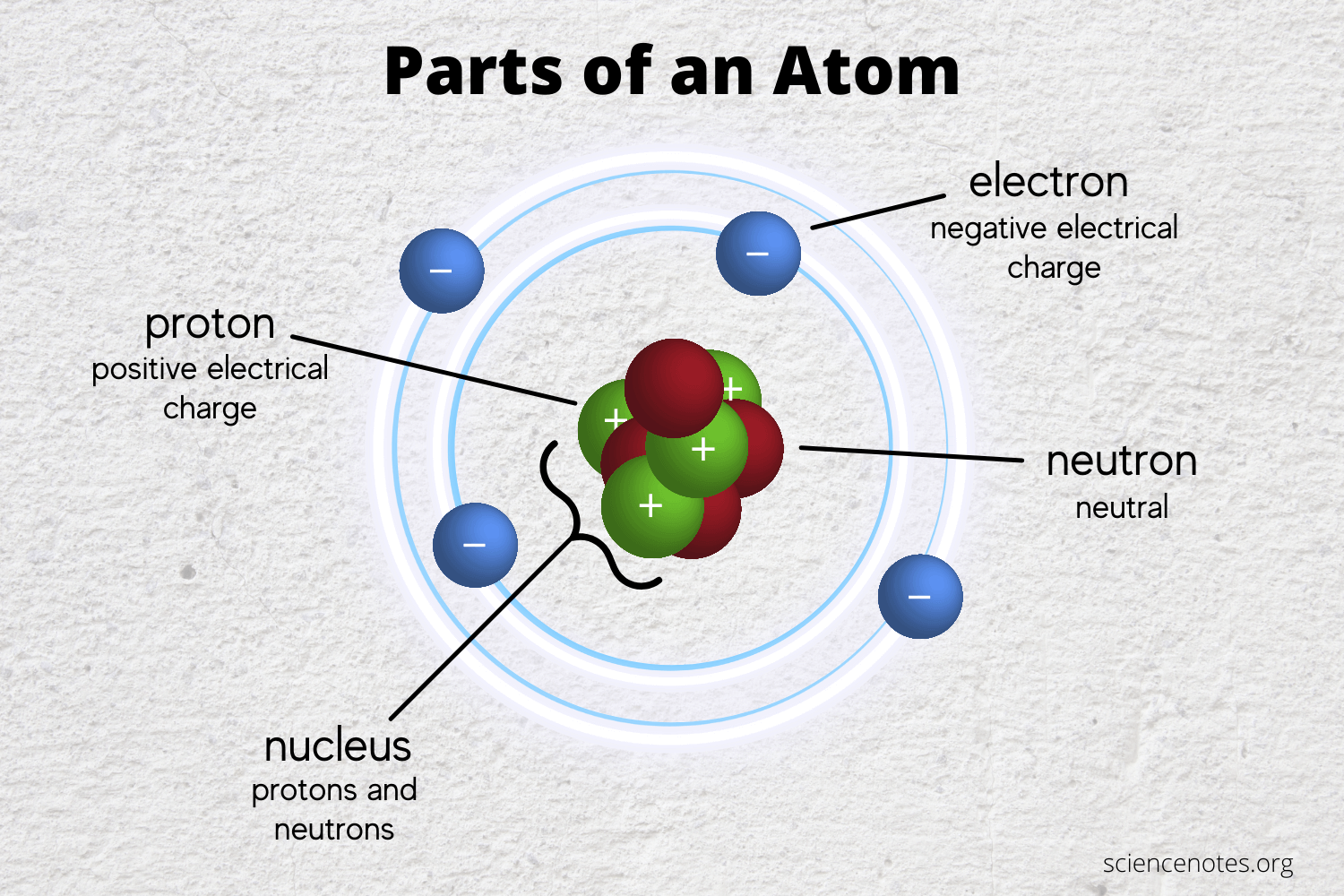
Learn the Parts of an Atom

Atoms & Molecules: e-chapter — The Biology Primer

What is an Electrophile? (with picture)

Ion | COSMOS
